Revolutionizing AI-nization: Multi-Agent Coordination and SWARM Technology for Intelligent Solutions

As artificial intelligence (AI) advances, new methods of harnessing its power are reshaping industries worldwide. OpenAI’s recently launched SWARM framework is one such breakthrough, allowing multi-agent systems to collaborate, coordinate, and dynamically adapt to complex workflows. SWARM technology marks a paradigm shift, particularly for multi-faceted businesses like Rakuten, enabling AI systems that can handle large-scale, cross-functional tasks with efficiency and precision. In this article, we explore SWARM’s potential applications, focusing on e-commerce and fintech—industries where automation and personalization are crucial.
Understanding SWARM Technology: A New Era of Multi-Agent AI
SWARM is a multi-agent framework that allows specialized AI agents to operate in tandem, each handling specific tasks within a larger, integrated system. This approach contrasts traditional AI models that require a single model to perform multiple tasks, which can limit scalability and lead to inefficiencies. With SWARM, OpenAI introduces modularity, allowing each agent to operate independently while coordinating with others, thereby optimizing task distribution across workflows.
In this setup, each agent is equipped with a routine tailored to its specialized functions. When tasks align with an agent’s expertise, it completes them autonomously, reducing response times and conserving system resources. However, for tasks requiring additional expertise, agents utilize handoffs: an intelligent routing system where tasks are escalated or reassigned based on complexity and context.
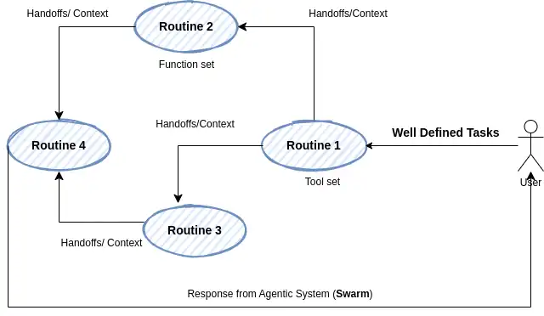
A pivotal advantage of SWARM lies in its intelligent “handoff” capability: tasks are dynamically routed between agents based on task complexity and context, with each agent making data-driven decisions about whether to complete the task or transfer it to another agent. This adaptability not only accelerates processing times but also maintains high efficiency by allowing each agent to focus on what it does best.
Research indicates that systems with similar orchestration approaches can improve task efficiency by up to 40% in high-traffic applications, such as e-commerce order processing and customer support.
For businesses, this modular, context-driven system ensures that routine, well-defined tasks are handled quickly, while complex tasks receive specialized attention. This efficiency is amplified through the integration of tools and functions that agents can access as needed, ensuring streamlined task completion and accurate escalations within the framework.
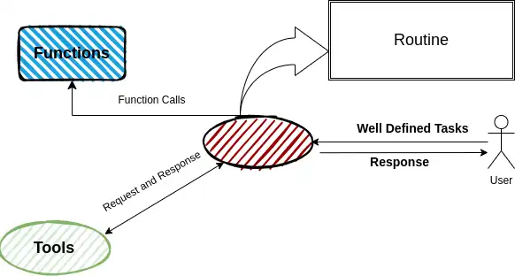
In complex, high-volume environments like e-commerce, where diverse, interconnected tasks are common, SWARM’s intelligent coordination fosters scalability and precision, driving faster and more reliable outcomes across multiple operational domains. This makes SWARM particularly beneficial for multi-functional enterprises, as it enables seamless orchestration of tasks, adapting dynamically to changing business demands.
The Role of Multi-Agent AI in Complex Business Operations
With SWARM, each agent is a domain expert. In a business environment where Rakuten manages e-commerce, fintech, and digital content, specialized agents can be deployed to oversee particular processes, such as customer inquiries, payment processing, and content recommendations. By assigning domain-specific agents, SWARM not only improves response accuracy but also reduces operational load on individual agents. This structure can improve response times by up to 30% in real-time applications, significantly enhancing customer experience in fast-paced sectors.
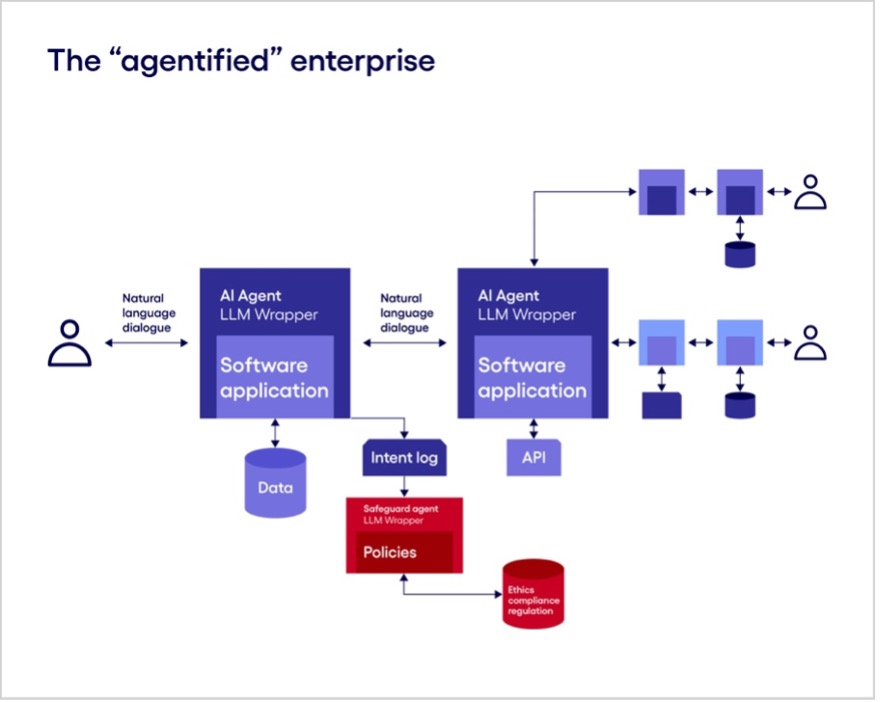
For instance, in a Rakuten-like e-commerce scenario, specialized agents could handle inventory management, order tracking, and post-purchase support individually, transferring inquiries seamlessly among them. Automated agent collaboration can thus reduce query resolution times and improve response accuracy, vital metrics in digital marketplaces where rapid and accurate responses drive customer loyalty and conversion.
Enhancing Personalization in E-commerce through Multi-Agent SWARM Systems
Personalization is central to modern e-commerce, where customers expect recommendations tailored to their preferences. Traditionally, achieving personalization required a single model to analyse user behaviour, match it with product data, and generate recommendations, which is computationally expensive. SWARM’s modular framework, however, enables specialized agents to handle different stages of personalization. For instance, one agent can analyse browsing history, another can process purchase patterns, and a third can handle real-time contextual recommendations. This division of labour allows SWARM systems to personalize interactions more accurately and at scale.
According to industry studies, personalization algorithms can increase conversion rates by as much as 50% when effectively tailored to customer behaviour.
For a platform with as many touchpoints as Rakuten, SWARM can optimize recommendations, providing a seamless experience that aligns with individual user preferences. This heightened engagement could lead to higher average order values and increased customer retention, both critical metrics in competitive online markets.
Driving Efficiency in Fintech Operations with SWARM
Beyond e-commerce, SWARM technology holds promising applications in fintech. With specialized agents, SWARM can manage complex processes like fraud detection, loan application assessment, and compliance checks, which require precision and rapid response. As financial transactions have become increasingly digital, the demand for secure, automated processes continues to grow. By breaking down tasks and assigning them to specialized agents, SWARM can ensure that each stage of financial processing is handled by a model optimized for that task, increasing both security and processing speed.
For a fintech operation, agent-based orchestration has been shown to reduce operational processing times by 25-35% in high-frequency transaction environments.
This advantage is particularly valuable for companies like Rakuten, where the integration of e-commerce and fintech means large volumes of transactions and compliance-sensitive data handling. SWARM’s structure could allow for near-instantaneous fraud detection alerts, for example, safeguarding customer trust and minimizing risk.
Challenges and Future Potential of SWARM in Business Applications
While SWARM offers substantial potential, there are limitations to consider. As a newly introduced framework, SWARM is still in its experimental phase. The framework currently lacks built-in memory, which limits its ability to maintain long-term context across interactions. Businesses deploying SWARM may need to develop workarounds or integrate with external memory solutions, especially for applications where long-term interaction history is crucial.
Nevertheless, the simplicity and modularity of SWARM make it highly accessible. Its open design invites customization, enabling businesses to adapt SWARM to their unique requirements. By potentially integrating SWARM with frameworks that support memory and context management, companies can build robust, flexible systems that expand SWARM’s capabilities.
Conclusion: SWARM and the Future of Intelligent Business Operations
SWARM technology exemplifies the future of intelligent, autonomous systems. With its multi-agent orchestration capabilities, it presents a solution that can streamline operations, improve response times, and enhance personalization in real-time. For a business like Rakuten, which encompasses diverse digital services, SWARM offers a strategic advantage in automating and optimizing multi-channel interactions.
As SWARM continues to evolve, it is poised to become a foundational technology in industries that value speed, accuracy, and tailored user experiences. For companies aiming to stay at the forefront of digital transformation, SWARM offers not only a technological advantage but also an opportunity to redefine the standards of intelligent business solutions.
References

Anant Govil | RIEPL
November 04, 2024

