Impact Of AI On Existing Job Market & Ethical Use Of AI
By: Siddhartha Das | RIEPL

AI won’t replace all jobs done by humans. AI won’t take your job, but those who embrace it will lead and take the opportunity.
- Jansen Huang, CEO of NVIDIA
The landscape of retail is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the advent of generative AI-based shopping agents. These sophisticated systems leverage advanced machine learning algorithms to provide consumers with hyper-personalized shopping experiences, transforming the way we discover, select, and purchase products. As AI technology continues to evolve, it offers unprecedented opportunities for both businesses and consumers, but also presents significant challenges that must be carefully navigated.
In this blog, we will explore how generative AI is reshaping the shopping experience, the impact on the job market, and the ethical considerations associated with these advancements. By understanding these dynamics, we can better appreciate the potential of AI to revolutionize e-commerce while addressing the accompanying challenges and ensuring responsible deployment.
The Evolution of AI in Shopping
Historical Perspective
The integration of AI into shopping has been gradual yet transformative. Early AI applications in e-commerce were primarily focused on basic recommendation systems, utilizing algorithms to suggest products based on past behaviour. Over time, these systems have evolved, incorporating more complex algorithms and larger datasets to enhance accuracy and personalization.
Key Milestones
- 2000s - Basic Recommendations: Initial recommendation systems provided simple suggestions based on user purchase history and browsing behaviour.
- 2010s - Advanced Personalization: The advent of machine learning and big data analytics allowed for more sophisticated personalization, including predictive recommendations and dynamic pricing.
- 2020s - Generative AI: The latest developments in AI, such as GPT-4 and other generative models, enable even more personalized and contextually relevant shopping experiences, from virtual try-ons to automated style recommendations.
Current Trends
- Hyper-Personalization: AI systems now offer highly personalized shopping experiences by analysing detailed customer data and predicting preferences.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: AI is increasingly being integrated with AR, VR, and IoT to create immersive shopping experiences.
Case Study: Designer Front - The Rise of AI-Generated Influencers
Background: Traditionally, fashion designers and brands have relied heavily on human influencers to promote their products. This process involved selecting influencers, negotiating contracts, and creating marketing campaigns, often requiring substantial time and financial investment. However, the advent of generative AI has revolutionized this approach by creating virtual influencers, thereby offering a cost-effective and highly customizable alternative.
Lil Miquela –

- Miquela is a virtual influencer created by Trevor McFedries and Sara DeCou.
- She was introduced as a 20-year-old girl of Brazilian-American heritage.
- Her Instagram profile presents her as a CGI model with a distinctive fashion sense.
- She collaborates with major fashion brands, including Calvin Klein and Prada, showcasing their products to a broad audience.
Impact
- Cost Efficiency: They are one-time investment in technology and creative content, as opposed to ongoing fees and negotiations with human influencers.
- Control and Customization: Brands have complete control over the influencer's image, message, and schedule.
- Scalability: Virtual influencers can be scaled infinitely, appearing in multiple campaigns simultaneously without logistical constraints.
Similarly, Amazon Alexa for customer queries, Lex product handles millions of conversations across English, Italian, Spanish, French, and German.
Impact on the Job Market
- Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI
The rise of AI in e-commerce is reshaping the job market. While AI enhances efficiency and personalization, it also leads to job displacement and the creation of new roles.
| Sector | Number of People Working Currently (global) | Salaries in billion (annually) | Money Saved Due to AI | People May Lose Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Service | 2.5 million | $80 | Substantial | Some roles may be at risk |
| Retail Management | 1.2 million | $50 | Notable | Certain tasks may change |
| Marketing & Advertising | 800,000 | $40 billion | Significant | Shifts in job roles |
| Supply Chain Management | 1 million | $60 billion | Substantial | Automation of processes |
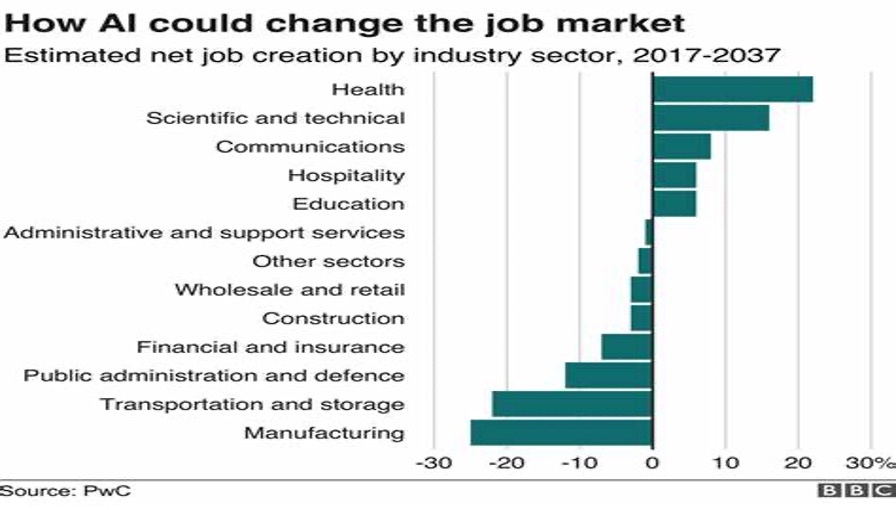
Job Sectors Affected
- Customer Service: Automation of customer support through AI chatbots and virtual assistants reduces the need for traditional customer service representatives. Approximately 20-30% of customer service roles may be impacted.
- Retail Management: AI-driven inventory management and predictive analytics streamline operations, potentially reducing the need for manual oversight. This could impact 10-15% of retail management positions.
- Marketing and Advertising: AI tools for targeted advertising and data analysis may lead to a decline in traditional marketing roles, though new positions in AI-driven marketing and analytics will emerge.
- Supply Chain Management: Autonomous systems and AI-powered logistics optimize supply chain processes, affecting roles in warehousing and logistics. An estimated 15-20% of these jobs may be impacted.
Skills and Opportunities
As AI transforms these sectors, there will be a growing demand for skills in AI development, data analysis, and ethical AI management. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives will be crucial for workers transitioning to new roles in the AI-driven economy.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Based Shopping Agents
"The challenge is to build AI that is safe, that is ethical, that is fair, and that is transparent.”
- Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Data Privacy and Security
AI-based shopping agents rely on extensive data collection, raising concerns about data privacy and security. It is essential to implement robust data protection measures, ensure transparency in data practices, and respect consumer consent.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Bias in AI algorithms can lead to unfair practices, such as discriminatory recommendations or pricing. To address this, regular audits of AI systems, diverse training data, and fairness-aware algorithms are necessary.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in AI decision-making and accountability for AI outcomes are vital for building trust. Companies should provide clear explanations of AI systems and establish accountability mechanisms.
Consumer Autonomy and Manipulation
AI's influence on consumer behaviour must be balanced to avoid excessive manipulation. Ensuring that recommendations are diverse and providing options for personalization adjustments are key to respecting consumer autonomy.
Impact on Employment and Economic Disparities
AI-induced job displacement and economic disparities must be addressed through reskilling programs and inclusive AI development practices. Social safety nets and policies will support displaced workers and promote equitable access to technology.
Balancing Innovation and Ethics
Regulatory Frameworks
Effective regulations are crucial for balancing innovation with ethical considerations. Policymakers must craft flexible, forward-looking regulations that protect consumer rights while fostering technological advancement.
Corporate Responsibility and Ethical Leadership
Businesses must adopt ethical AI principles, establish ethics committees, and engage with stakeholders to ensure responsible AI practices. Transparency and accountability in AI systems are essential for maintaining consumer trust.
Consumer Rights and Empowerment
Informed Consent and Transparency: Consumers have the right to know how their data is being used and the extent of AI's influence on their purchasing decisions. Informed consent involves providing clear, accessible information about data collection practices and obtaining explicit consent from users. Transparency about the workings of AI systems, such as recommendation algorithms and dynamic pricing models, empowers consumers to make informed choices.
Control Over Personal Data: Consumers should have control over their personal data, including the ability to access, modify, or delete their information. Providing users with easy-to-use tools to manage their data preferences is essential for respecting their privacy and autonomy.
Addressing AI-Induced Harms: In cases where AI systems cause harm, whether through biased recommendations, data breaches, or other issues, consumers should have avenues for redress. This includes clear processes for lodging complaints, seeking compensation, and holding companies accountable for their actions.
Ethical AI Design and Development
Designing AI systems with fairness, explainability, and safety in mind is essential for responsible AI development. Companies should prioritize bias reduction, interpretable models, and robust security measures.
Public Discourse and Education
- Raising Awareness: Public discourse and education play a vital role in shaping the ethical landscape of AI. Raising awareness about the ethical implications of AI technologies, including both their benefits and risks, can help foster informed public debate.
- Promoting Digital Literacy: Educating consumers about AI technologies, their capabilities, and their limitations is essential for empowering them to make informed decisions. Digital literacy programs can help consumers understand how AI systems work, what data they collect, and how to protect their privacy.
- Ethical AI Advocacy: Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), academic institutions, and advocacy groups have an important role in promoting ethical AI practices. These organizations can conduct independent research, advocate for fair regulations, and provide resources and support for consumers and businesses.
Conclusion
AI is one of the most important things humanity is working on. It is more profound than, I dunno, electricity or fire.
- Sundar Pichai Google CEO
The future of AI-based shopping agents promises significant advancements in personalization, convenience, and efficiency. Balancing innovation with ethical considerations, transparency, and consumer rights will be crucial for realizing the full potential of AI while promoting a fair and equitable e-commerce landscape. Collaboration among businesses, regulators, and consumers will be essential in shaping a positive future for AI in shopping.
Reference
https://www.instagram.com/reel/C5jWcPzP3wQ/?img_index=welcome.ai
https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2024/06/04/boon-or-bane-navigating-the-impact-of-ai-on-the-job-market/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wem2zDvFj4Y
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miquela
https://www.bbc.com/mundo/noticias-49906421
https://www.cut-the-saas.com/ai/the-ai-behind-virtual-influencer-lil-miquela
https://aws.amazon.com/lex/customers/
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/4/2332
https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2024/07/ftc-submits-comment-fcc-work-protect-consumers-potential-harmful-effects-ai
https://connexion3.gr/ai-will-create-as-many-jobs-as-it-displaces-report/

Siddhartha Das | RIEPL
August 08, 2024

