Gen AI in Transforming Music Streaming Platforms
By: Bhavya Neelgar, Rakuten India
Introduction of R-Music
Rakuten’s Music Streaming Platform offers 100 million songs and a range of subscription plans, from free to monthly and yearly options. With over 120,000 paid subscribers using our app and web services across Japan, we're now tackling some classic and complex challenges using Generative AI. I'll walk you through how we can rethink basic functionalities to solve these challenges with Generative AI.
High Level Components Involved In Any Music Streaming Application
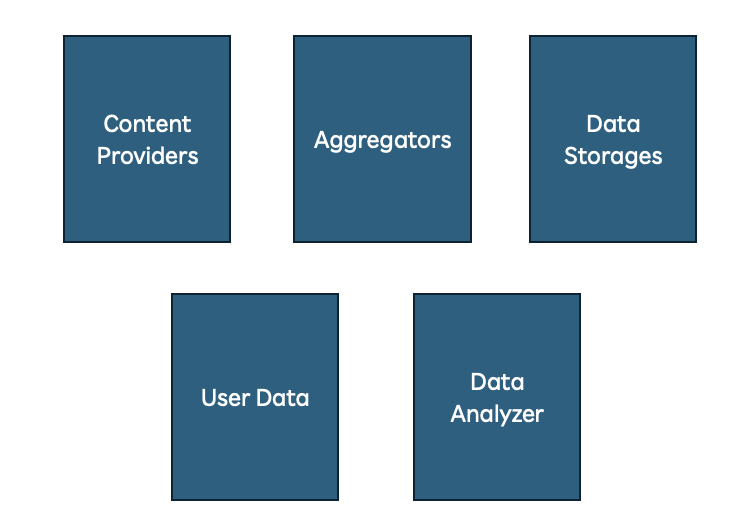
- Content Refinement/Enrichment: Content provided by various label companies may lead to duplicates and inconsistent metadata categorization. This affects how content is classified, such as by style, mood, genre, or tempo. Using Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on diverse datasets can help classify content into these categories more accurately.
- Search: Traditional search systems might not deliver the most relevant results. Instead, we need to implement semantic search, which understands the user's intent and context based on the keywords they provide and their search history. Semantic search can provide more accurate and context-aware results.
- Recommendations: In today’s competitive streaming market, recommendations should not only be based on the user’s history but also on current internet trends. Real-time recommendations can be enhanced through AI-powered recommendation engines that adapt to user preferences.
- Playlist Creation: Generative AI algorithms can accelerate playlist creation for both users and operators. By learning from user actions and external sources, these algorithms can map data back to internal systems to generate more personalized playlists.
- User Feedback/Customer Engagement Tracking: Building a robust system that continuously collects user feedback from external platforms, like social media, is essential. This approach goes beyond traditional customer support queries, making it a fundamental requirement for any modern service.
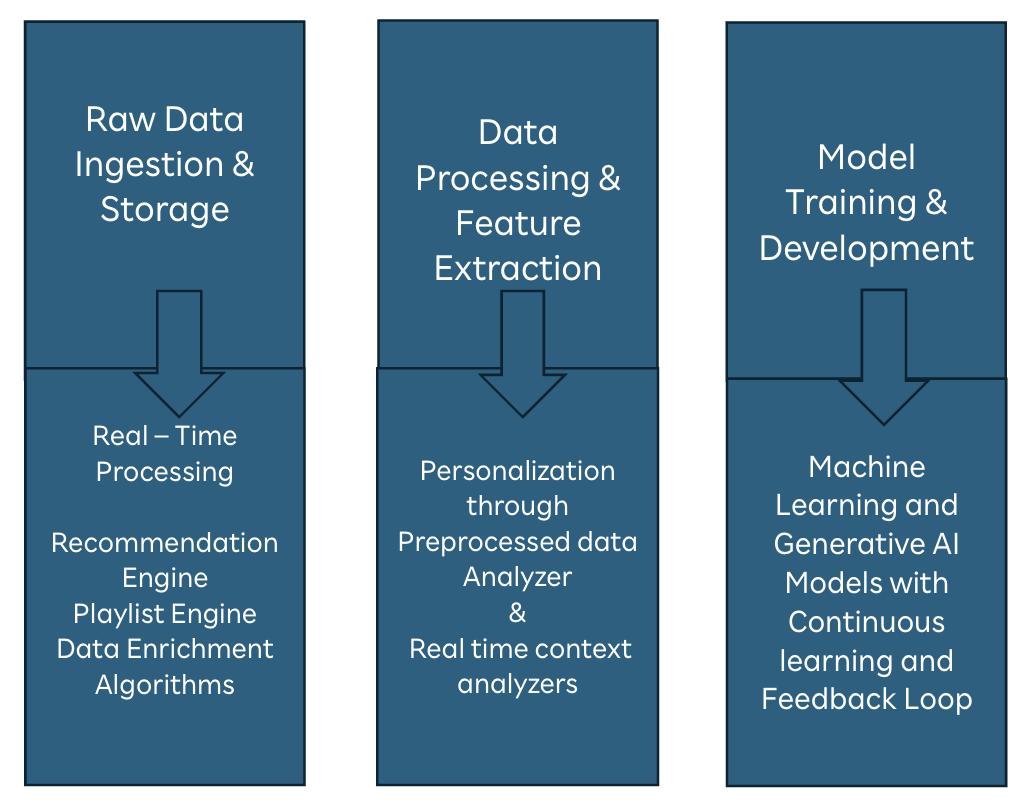
It can be majorly categorised in 3 components – Data Ingestion, Data Processing, and Model training.
How would Lana Del Rey’s songs sound if sung by Jim Morrison? Before the generative AI boom, this was purely a matter of imagination. Today, however, AI-generated music is becoming a reality, with new channels and music apps allowing producers to test and bring their ideas to life with minimal resources. While some people have reservations about AI-generated music and how it might sound, the reality is that we’re reaching a point where it’s difficult to distinguish between the original artist and their AI clone.
However, these new possibilities come with significant regulatory challenges. Will AI-generated music be eligible for copyright protection? Does creating a song that mimics a famous artist violate copyright law? Can artists restrict the use of AI-generated versions of their voices? Currently, there are insufficient regulations to address these questions, but as the AI music trend continues to grow—and it likely will—new legal frameworks will be essential.
Artists may also seek legal action to prevent machine learning models from using their music for training purposes. As AI-generated content featuring artist clones becomes more prevalent, it's clear that new regulations will need to emerge soon to address these complex issues.
Conclusion
While Generative AI presents exciting new possibilities, it also requires the creation of appropriate regulations to address emerging legal and ethical challenges. It's essential that we use this technology responsibly, protect our data, and remain mindful of its implications.

Bhavya Neelgar | RIEPL
August 19, 2024

